Introduction
The current digital printing landscape is crowded with various methods worthy of consideration. But if you look closer, one method will grab your attention more than the others: heat transfer printing.
Also known as thermal printing, this relies on heat and pressure and transfer papers. It’s a method widely known for its versatility and crisp designs. While other methods are limited to one or two substrates, thermal printing applies to a full range of printable surfaces.
You’ll notice them for a handful of applications. One is textile printing, which is its most popular use. It’s also common for signage, decals, home decor, and accessories.
Learn more about this go-to method for hobbyists and small businesses in this blog.
What is Heat Transfer Printing?
As the name suggests, heat transfer printing involves using heat and pressure to create designs. It includes printing on a transfer film or paper before running it through the heat press for the final transfer.
In essence, thermal printing loosely refers to any method that uses high temperatures for design transfer. Any technique that uses transfer films and a heat press qualifies as thermal printing.
Under this are sublimation, vinyl, DTF, and inkjet/laser heat transfer printing. Individually, these methods are popular for their versatility, high-resolution transfers, and accessibility. On the downside, however, they’re not the most durable prints.
The Process of Heat Transfer Printing
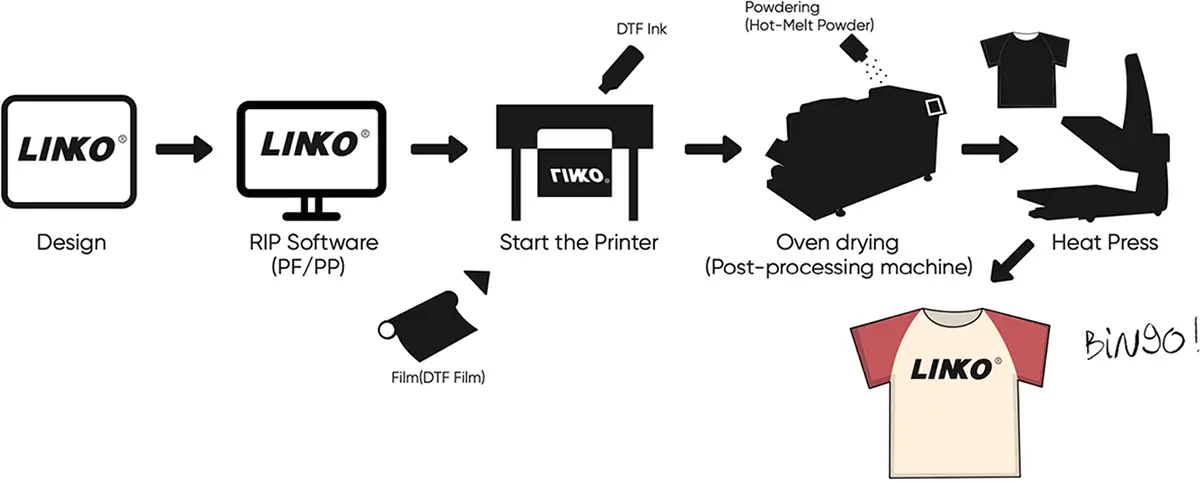
Here’s how to do heat transfer printing.
1. Design Creation
Like in every printing technique, the process commences with designing your digital image. For more design freedom, you can use RIP software to create your image how you like it. The most common graphic design software include Caldera, Onyx, Flexi, and Printfactory. Relying on these illustrators gives you better customization and limitless image ideas.
2. Printing the Design
The next process is to transfer your digital design to heat transfer paper. You can choose between various printer types, such as sublimation, inkjet, DTF, or laser. These techniques are all subtypes of heat transfer printing.
You still have to remember that some methods can proceed directly to heat transfer after printing. But others still need some extra steps, like in DTF. After film printing, you must still apply and cure an adhesive powder using heat. Ink must stick to the fabric.
3. Heat Application
At the heart of each heat transfer printing method is the heat application. It’s where your design ideas are brought to life by turning them into actual shirt designs.
You need to run your printed film on a heat press machine for this process. This process melts the ink, letting it bind with the fabric and transfer completely. Make sure you’re following the prescribed heat and pressure configuration for every method. Each technique has different ink and film type, hence, one method’s configuration wouldn’t always work out with the other.
It’s best to refer to the heat press’s recommended setting or the transfer’s film’s prescription. You can also experiment first to identify the most suitable temperature.
4. Cooling and Removal
There are two types of transfer film: cold peel and hot peel. When you use a cold peel film, you need to cool it down for a few seconds before peeling it. In contrast, you can instantly peel a hot peel film right after running it on the heat press.
You must observe the proper peeling based on the peel type as it ensures durable and damage-free transfer. Peeling too early or too late can prevent designs from sticking or warping.
Advantages of Heat Transfer Printing
These sought-after methods stem from the profound perks that heat transfer offers. Here are the upsides to using heat transfer printing.
Versatility
Besides printing on fabric, you can also transfer your designs to ceramics, glass, or metal. This wider canvas availability makes any heat transfer method suitable for many printing needs. And even if you stick to fabric printing, you can still work on most fabric types. Like in DTF, you can print either on natural, synthetic, or blended fabrics.
The method’s versatility makes it a go-to for those wanting an all-around printing business. It’s best for printing on fabric, bags, wallets, and mugs.
Cost-effectiveness
Ask any seasoned heat transfer printer, and they’ll likely tell you it has one of the best value for money. Its initial setup alone costs less than methods like embroidery or screen printing. Not to mention, the materials and supplies are more available and affordable, as well. On top of that, it requires fewer steps and remains economical for small-scale printing.
Heat transfer printing is often more popular for those just starting out their printing business. It’s also more affordable if you’re after t-shirt printing for a hobby or personal use.
Vivid Colors and Intricate Designs
Another crucial aspect that heat transfer printing excels on is the print quality. It produces the sharpest colors, even on the most complex images. Take, for example, the quality you get from a DTF or sublimation print. Both deliver high-resolution transfers and the sharpest results, among other methods.
Ease of Use
Heat transfer printing is also a straightforward process. It’s easy enough to be an entry point for those wanting to enter the world of printing. You can do it with little to no expertise without the need for advance tools or equipment. Doing it at home is very workable provided you have your printer, consumable supplies, and a standard heat press machine.
Disadvantages of Heat Transfer Printing
Despite the undeniable upsides of heat transfer printing, it still comes with some drawbacks. Here are the unwanted side of this method.
Durability Issues
The durability of heat transfer prints is one of its major concerns. While it produces crisp and vibrant images, the finished product remains vulnerable to cracking and peeling. This is a common encounter with printed garments. The prints degrade faster than methods like screen printing. But you can still ensure that your prints do not fall off prematurely by following the method’s proper procedure and settings.
Time-Consuming
While heat transfer is a straightforward technique, heat pressing remains time-consuming. Running each transfer paper on the heat press machine takes significant time, especially in large batches. Moreover, other methods need individual treatment of the substrate and the film. This further slows the process as any step can’t be set aside or shortened.
Not Suitable for High-Volume Printing
The method’s time-consuming nature makes this technique not suitable for mass production. It requires several manual processes that’s simply not ideal for large-volume printing.
Comparison With Other Printing Methods
Here’s how heat transfer printing compares with other printing methods in the market.
Screen Printing
Screen printing takes the upper hand in efficiency. It caters to large runs due to its ability to print in bulk. It produces more durable and lasting prints, as well. However, there are downsides to this method, too. One is that it needs more setup time for preparing the design, making it less ideal for custom designs. Also, screen printing is not suitable for detailed or multi-colored designs.
Direct-to-Garment (DTG) Printing
DTG printing uses inkjet technology to print designs direct to the fabric. This makes it ideal for producing high-resolution, full-color images, especially on cotton fabrics. The major caveat is that it’s an expensive and less accessible method. DTG calls for specialized equipment that are not small-business friendly.
Embroidery
Without a doubt, embroidery produces the most durable designs for t-shirts. It stitches the design using thread, commonly used for logo-making and text-based prints. But, the versatility is just missing. Unlike heat transfer, which works with rigid surfaces, it’s often limited to printing on soft substrates. Embroidery also struggles with fine lines or intricate designs.
This method can also be time-consuming and expensive.
Conclusion
There are clearly positive and negative sides to heat transfer printing. Your printing needs should ultimately determine whether it’s the right method for you.
You should seriously consider investing in this technique if you’re after vibrant and sharp designs. And you should never think twice about choosing this if you’re looking for a versatile method. If you’re after practical and affordable printing, this should also be on your list.
But, if durability is your key consideration, thermal printing will not serve you well. This technique is also not suitable for mass production. So, only choose this method if you’re getting into printing as a hobby or a small business venture.

