Introduction
Traditional DTF printing is still one of the most widely used printing methods. However, with the development of printing technology, traditional DTF printers can no longer meet market demand, such as DTF printers cannot directly print mobile phone cases. In order to make up for this shortcoming, UV DTF printers came into being.
DTF suits soft surfaces such as T-shirts, while UV DTF suits hard surfaces such as mugs. Traditional DTF printers can produce colorful shirt designs due to their compatibility with white ink. It works well with almost all types of fabrics, but not with hard materials, which is where UV DTF printers come in.
DTF and UV printing differ in their processes, materials, and costs. This guide will explore these two printing methods more.
What is DTF Printing?
Direct-to-film printing is where you print your design on a film before pressing it on a canvas. A DTF printer uses inkjet technology like other digital printing methods. But, DTF printing is more popular since it’s versatile and inexpensive.
Traditional DTF tailors to soft substrates such as t-shirts. Unlike DTG printing or sublimation, DTF printing works on most fabric types. It also works on various colored shirts via heat.
New methods rise relative to market growth, owing to the principles of DTF printing. However, the traditional DTF printing method remains as lively as ever. In 2022, the global market for digital textile printing will be USD2.6 Billion. According to Alibaba, DTF printing occupies 67% of this global figure.
What is UV DTF Printing?
UV DTF printing is a new printing method rooted in the principles of DTF printing. It harnesses ultraviolet curing technology to transfer designs on rigid substrates. But instead of using pigment ink like in DTF, UV printing lays UV-curable ink on a transfer film.
UV printing is a DTF printing subtype, although it differs from traditional DTF. One significant difference is how they transfer designs onto a material. UV printing does not use a heat www. Instead, you press the design from the film onto the material by hand to paste the image. The designs come in the form of stickers. The image sticks to the surface once peeled and pressed.
Today, market outlooks indicate a promising future for the UV DTF printing industry. Such positive growth owes to the method’s versatility, extensive application, and cost-efficiency.
Differences Between DTF Printing and UV DTF Printing
| DTF Printing | UV DTF Printing | |
|---|---|---|
| Consumables | DTF printer, DTF powder, DTF ink, Powder shaker, Curing oven, Heat press machine | UV DTF Printer, AB film, UV ink |
| Working process | 1. Design 2. Print and Powder coating on film 3. Shake powder 4. Heat press transfer 5. Tear off the film |
1. Design 2. Print on A film 3. Laminate B film 4. Cutting 5. Paste on items |
| Suitable Surface | Soft Surfaces (T-shirts, Hoodies) | Hard Surfaces (Luggage, Mugs, Phone Cases) |
| Ink Type | DTF ink | UV ink |
| Applications | Clothing, Textiles | Luggage, Mugs, Phone Cases, and other hard objects |
| Cost | Relatively Lower | Relatively Higher |
Traditional DTF and UV DTF have few similarities. Both prints are on special transfer films, but the process and application differ. Here’s how they compare:
Supplies and Equipment
To do any of the two means buying specific supplies that are not interchangeable. Here is a list of what you need:
- Printer Machine
In traditional DTF printing, an ordinary inkjet printer can do the job. However, you still have the choice of a more advanced and integrated DTF printer. Still, the bottom line is that the DTF printer machine is more affordable than other methods. You can start printing your design with an inkjet printer with six ink tanks to store the white ink.
This is not the case for UV printing. The UV DTF printer is specifically a digital UV flatbed printer. The printer inks the design pattern once the film is on the flatbed. The UV link instantly cures as a UV lamp passes over it. Unlike traditional printers, a UV printer is more often used to print on rigid materials.
- Transfer Film
The main difference in transfer film usage is that UV printing needs two different films. The first one is the A Film, a self-adhesive PET transfer film. The B film will then be laminated with the A film to produce the design stickers.
However, DTF printing uses only one transfer film. Unlike ordinary PET film, DTF transfer films have an ink-absorbent coating. This is why DTF films present a matte frosted finish rather than transparent.
- Ink
Traditional DTF printing uses pigment ink that is compatible with inkjet printers. These inks come in cyan, yellow, magenta, black, and base white ink. Among the DTF inks provided by Linko, the white ink has excellent purity. The raw materials used in the ink come from the same supplier as Epson ink.
UV printers need UV ink. These UV-curable inks have different categories depending on the application. UV inks can be soft, hard, or flexible inks. Soft inks are for more delicate substrates like silicon phone cases. The hard UV ink applies to hardwood, metal, or glass materials. Flexible inks are often used for leather canvas.
- Laminating Machine
UV DTF printing uses a laminating machine to paste films A and B together. After printing on the transfer film (A), the PET film (B) sticks on top of it.
The laminating machine does its job with convenience. Although manually sticking together the two films also works if you lack a laminating machine.
- Curing Oven
Traditional DTF printing doesn’t need a laminating machine but a curing oven.
After the DTF transfer film is printed and powdered, it goes through an oven to cure the adhesive powder. You can also use the heat press as an alternative to the curing oven.
- Adhesive Powder
The adhesive powder is also exclusive to DTF printing. It is a unique powder applied evenly on the newly printed transfer films. This powder helps the ink to stick to the garment once heat-pressed.
Process
The process for DTF and UV DTF printing is also very different. Aside from printing on a film, the succeeding processes differ in many aspects. Let’s look at their respective process below.
DTF Printing
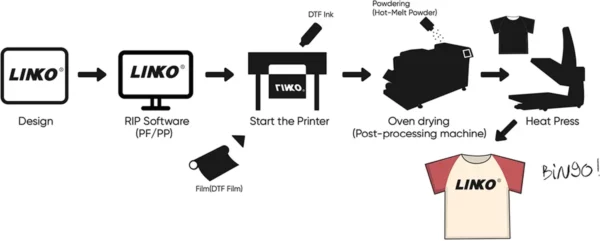
- Preparing the design. By using RIP software, you can create your design ideas. DTF printing owes its flexibility to the freedom of designs you can make. It works on white ink and many colors, so your design can range from simple to complex.
- Printing on transfer film. Once the design is all set, you can load your transfer film and print on it.
- Powdering the transfer film. You need to apply the adhesive powder while the ink is still wet. This will help the ink bond stronger to the shirts, making a durable transfer.
- Curing the adhesive powder. After its application, you need to cure the adhesive powder. You can melt the adhesive powder using a curing oven or a heat www.
- Pre-pressing the shirt. This refers to heat pressing the shirt for two to five seconds. This flattens the printing surface of the shirt and removes traces of moisture.
- Transferring. Press your design onto the shirt for 15 to 20 seconds at around 170 degrees Celsius. This melts and bonds the ink on the garment.
- Peeling. Once the design is pressed, remove the transfer film and trash it. Transfer films are single-use and are not printed on more than once.
UV DTF printing

- Preparing the design. You can use RIP software to design simple to intricate designs.
- Printing the design. Print your design using a UV flatbed printer. The process should be printing white ink first, then colored ink and varnish.
- Laminating. Laminate transfer films A and B using a laminating machine. You can also operate lamination manually.
- Cutting the design. You can manually or machine cut your design. Take note of the dimensions of the substrate you are printing on. Make sure the cut-out lies on the material properly.
- Pressing the sticker. First, remove the sticker’s film cover. Press the sticker onto the substrate using your finger until the design is pasted on. Slowly remove the film, and your design will be all set.
Applications of DTF vs. UV DTF
DTF printers are the go-to for printing on soft substrates like T-shirts, while UV DTF is for rigid substrates like wood panels and glass. Here are other materials that the methods are often used for.
UV DTF Printer
- Phone cases
- Mugs and glass
- Package boxes
- Tumbler/ bottle
- Luggage
- Tile panels

DTF Printer
- Hoodies
- T-shirts
- Tote bags
- Hats
- Pants

Pros and Cons of DTF and UV DTF Printing
DTF and UV DTF printers also have advantages and disadvantages. Below, we compare the advantages and disadvantages of the two methods.
Pros and Cons of DTF Printing
Pros:
- Vibrant and durable prints
- Versatile fabric choices
- Prints simple to intricate designs
- Fast Printing
- Cost Effective
Cons:
- Plasticized printed feel
- High initial cost for specialized equipment
- Limited to soft substrate
Pros and Cons of UV DTF Printing
Pros:
- Straightforward transfer process
- Compatibility with various rigid substrate
- High-quality prints
- Cost-efficient and simple
Cons:
- Limited to flat and rigid substrates
- Special UV ink requirement
Conclusion
Choosing between a DTF printer and a UV DTF printer must be a guided feat. Understanding which one will best serve your domain and market is essential.
If you are to pursue a t-shirt printing business, go with a DTF printer. This machine is specifically for printing on soft substrates and has a high profit margin. So how do beginners choose a DTF printer?
But if you are into printing on hard substrates like mugs and bottles, go with UV DTF. Here is a list of the 5 best UV DTF printers for start-ups.
Both machines offer practical solutions to your printing needs. Get in touch with Linko’s team of experts to help you choose the best printer for your business.

